FEATURED SENIOR DESIGN PROJECTS
Fall 2025 Projects

Project Summary
This report presents solutions to improve tooling organization and calibration management at Alstom’s West Mifflin facility. The primary objective is to reduce non-value-added time and improve overall production efficiency by addressing issues of misplaced tools, poor 5S implementation, and ineffective calibration tracking.
To complete the project, the student team followed a five-phase framework – Define, Analyze, Propose, Control, and Finalize – adapted from the Lean Six Sigma DMAIC methodology. During the Define phase, the team observed the current state, defined the scope, and created a project charter. The Analyze phase involved data collection and analysis to prepare for the solution presentation of the Propose phase. The team developed two main deliverables: improved tooling organization proposals and a Power BI dashboard to track tool calibration. The Control phase consisted of incorporating client feedback and making necessary adjustments to ensure successful implementation of the proposed solutions. The Finalize phase included creating implementation plans, finishing established deliverables, and giving ownership of the project to Alstom’s team.
The team’s final proposal included an updated Power BI dashboard, personal tool bags for operators at each station to eliminate transportation waste, updated shadow boards, new lockers for the facility, and color-coded tool cabinets at each station to store larger tools. The proposal was supported with data collected in the Analyze phase in the form of a utilization study and MOST analysis. The total savings are projected to be $95,508 over one year, with an initial implementation cost of $21,089 and anticipated savings of $105,818.
Project Summary
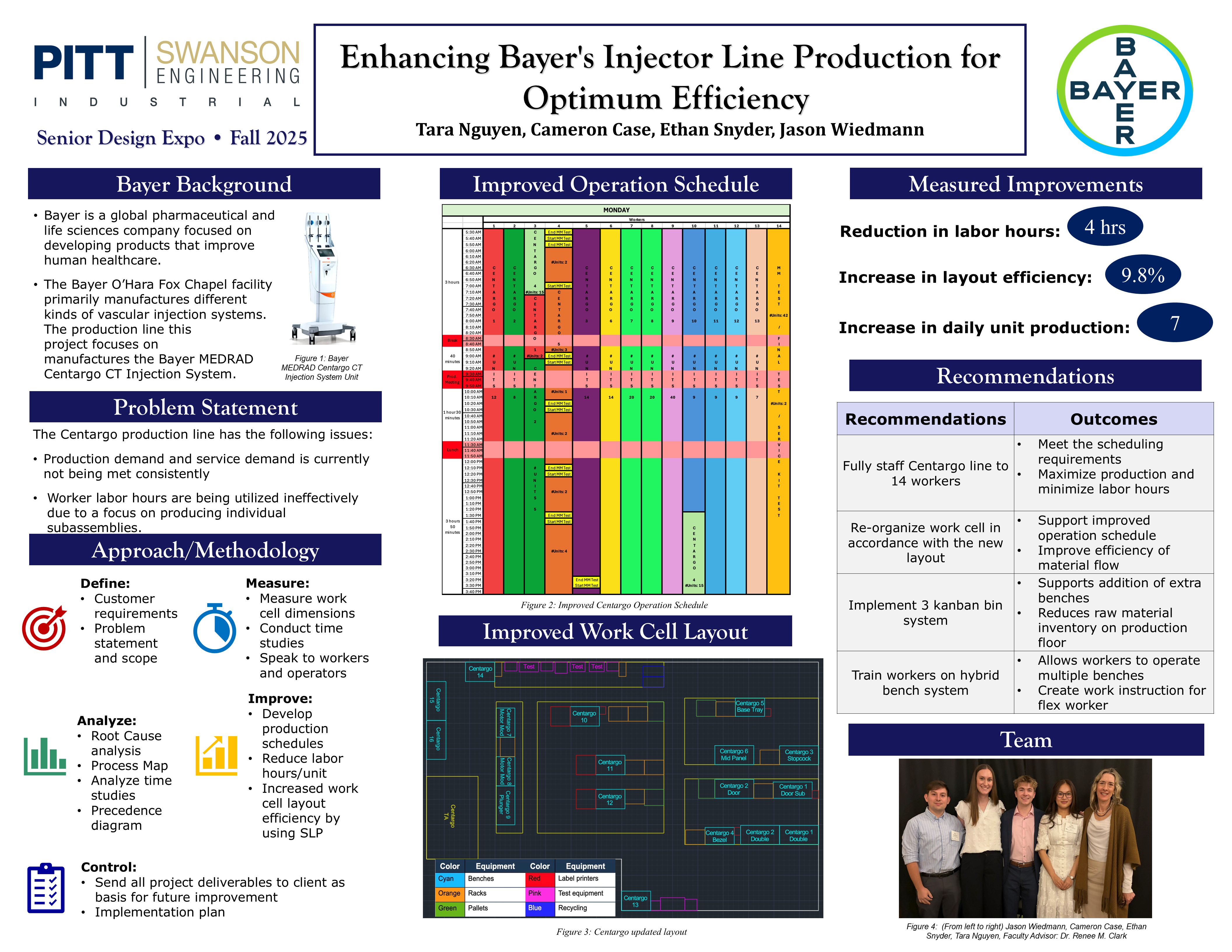
This report presents the process of designing a production schedule and optimized facility layout for the MEDRAD Centargo CT injection system production area at the Bayer O’Hara plant. The primary goal is to increase the production of the line through scheduling and layout adjustments. We aim to meet a daily production goal of at least six Centargo units per day.
We utilized the Lean Six Sigma DMAIC framework to structure our project. In the Define phase, we worked with our client to establish the project goals and the areas we were able to improve upon. We also established project roles within our team. Our Measure phase involved collecting time study data from each workbench in the production line, as well as measurements of the physical space to develop a diagram of the current layout. With this data we moved into our Analyze phase where we obtained the standard process times for each workbench and determined the current layout efficiency. In our Improve phase we developed a schedule to increase production and a new facility layout the increased efficiency. Finally, our Control phase focused on ensuring a smooth transition to our proposed recommendations as well as methods to ensure our recommendations are sustained.
The final deliverables for this project consist of a production schedule that satisfies current demand, and an improved layout of the work cell. The final deliverables will also include an Excel file detailing our calculations and schedule recommendations. This is intended to allow Bayer to further understand the schedule development process and provide a basis for further improvements to the production line.
Project Summary
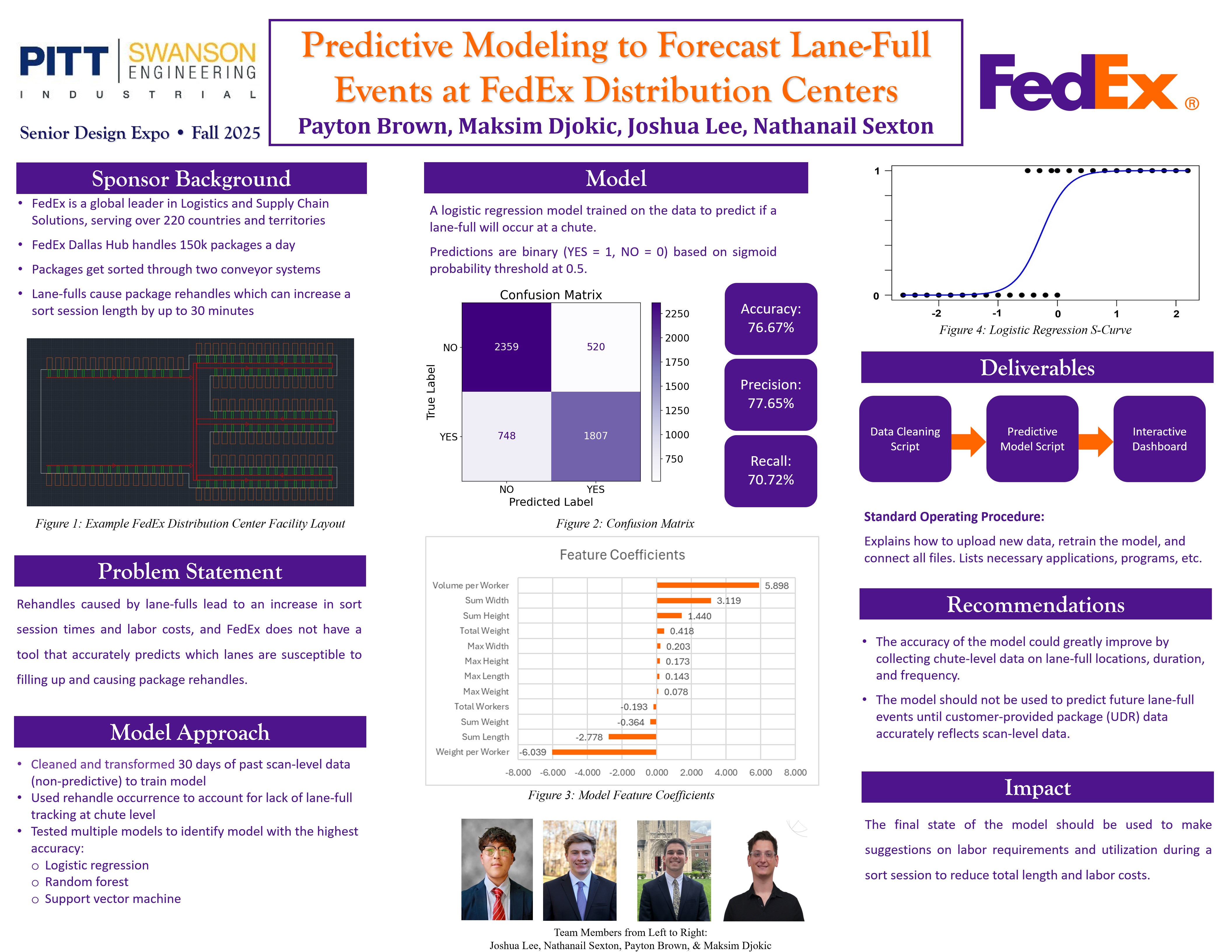
FedEx’s operation faces signficant challenges within their automated distribution hubs due to lane-fulls and package rehandling. A lane-full occurs when an outbound chute reaches its maximum capacity. This causes any packages sent to that chute to recirculate through the system repeatedly until the lane-full is cleared. Each recirculation for a package is known as a rehandle, which results in a slow down of the package sorting process. The FedEx network currently experiences 10% lane-fulls and 21% rehandles, and their target levels are 2.5% and 13.8% respectively. The team worked on the development of a predictive modeling solution to forecast lane-full events based on pre-sort session information. The solution enables FedEx supervisors to make proactive decisions regarding staffing and resource allocation instead of reactive responses.
Problem: FedEx does not have a tool that accurately predicts which chutes are susceptible to lane-fulls, and rehandles caused by lane-fulls lead to a decrease in throughput and an increase in sort session times and labor costs. Insights into where lane-fulls occur based on pre-sort session data can allow FedEx to adjust labor accordingly to reduce their effect on operational inefficiencies.
Approach: Utilizing an iterative framework specifically designed for data science problems, the team developed a predictive model using 30 days of historical data with millions of package scans, package dimensional records, and labor records.
Deliverables:
- Predictive model, built in Python, that forecasts lane-fulls for specific chutes during sort sessions.
- An interactive Power BI dashboard, with the predicitve model integrated, displaying chute-level predictions, KPIs, and risk metrics.
- Standard Operating Procedure providing in-depth steps, enabling FedEx to maintain and refine model for future.
Impact: The team provided the client team with a scalable, data driven tool, that can be implemented within a distribution hub for better labor allocation and scheduling. The model establishes a baseline for a lane-full predictive model, which can be further improved through data quality and availability.
Project Summary
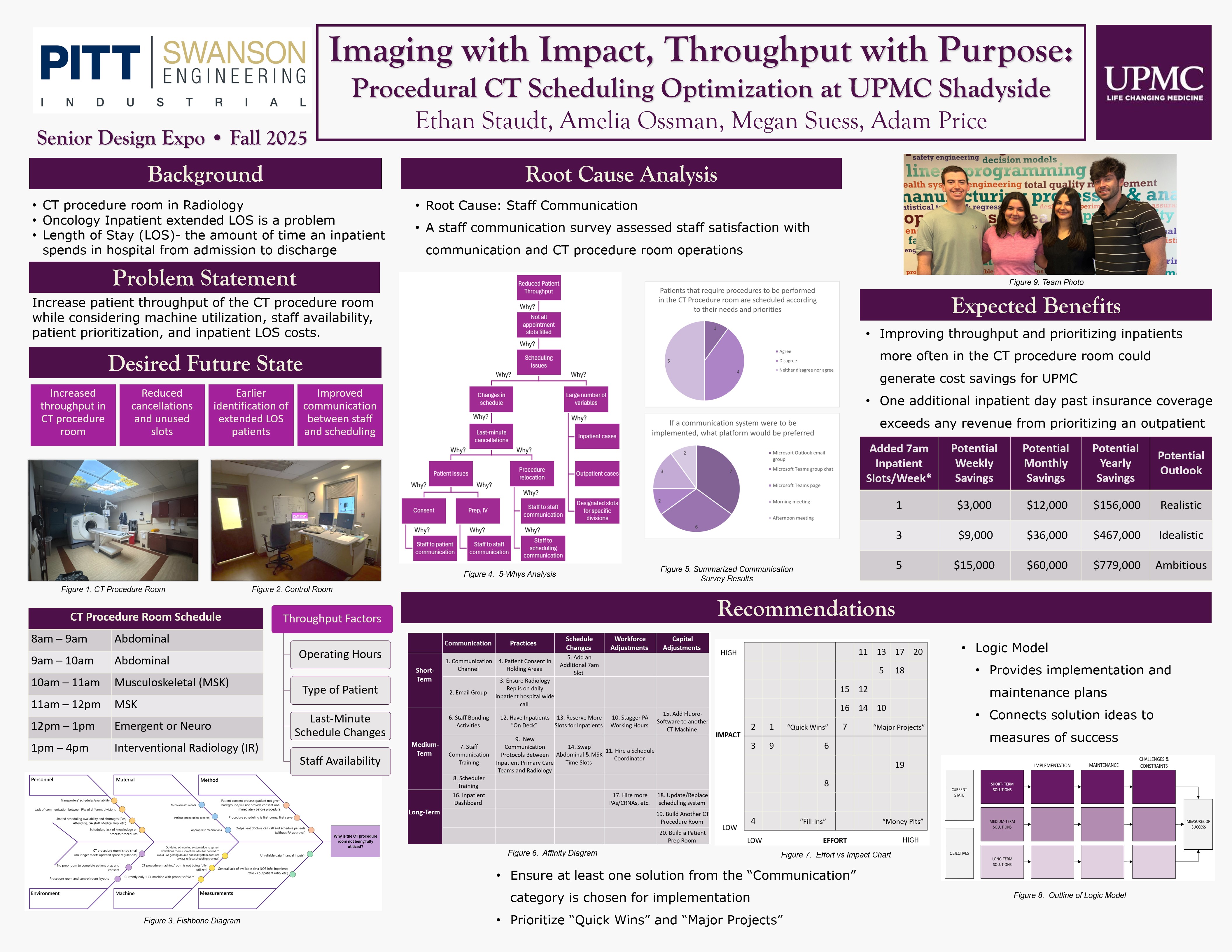
This project focuses on reducing oncology inpatient length of stay (LOS) by improving operations in the radiology department, specifically in the CT procedure room. The problem statement is: How can we implement changes to the CT procedure room scheduling and processes to increase patient throughput while also considering machine utilization, staff availability, patient prioritization, and inpatient LOS costs?
This project was executed using the DMAIC framework-Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. The Define phase involved developing an understanding of the medical terminology and operations within radiology to clarify the problem statement, project scope, objectives, and client expectations. In the Measure phase, the team conducted several visits to observe operations, interview key staff, and identify areas with improvement opportunities. In the Analyze phase, the team conducted root cause analyses, surveyed CT procedure room staff, and evaluated CT procedure room scheduling processes to identify waste and areas for improvements. In the Improve phase, the team brainstormed and categorized solutions for the CT procedure room. In the Control phase, the team developed recommendations detailing various potential solutions, implementation plans, and proposed data collection and metrics for the CT procedure room.
The findings from the root cause analysis revealed that lack of communication between staff-to-patient, staff-to-scheduling, and staff-to-staff, were the underlying causes contributing to limited patient throughput and underutilization of the CT procedure room. General LOS cost research was conducted, and the main finding was that one inpatient day past insurance coverage likely exceeds revenue that comes from prioritizing an outpatient. Using researched values, a cost analysis was performed for solution ideas focused on inpatient prioritization in the CT procedure room to quantify expected benefits on LOS.
Twenty potential solutions for inefficiencies in the CT procedure room were developed. The solutions were organized by category (communication, schedule changes, practices, workforce adjustments, and capital adjustments) and timeframe (short term, medium term, long term). The solutions were put into an Effort vs. Impact Chart to assist in prioritizing for implementation. A logic model was developed detailing implementation and maintenance plans for solution ideas.
The team recommends that UPMC adopt at least one communication-focused solution, given communication was the root cause of persistent issues. The team also recommends UPMC begin with implementing solution 1 (Communication Channel) and solution 2 (Email Group) first, as they are high impact, low effort, and could be implemented in the short term. Based on the research findings and cost analysis, the team recommends that UPMC strongly consider solutions that prioritize inpatients in the CT procedure room. While all formulated solutions seek to increase overall patient throughput, solutions 5, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, and 16 are most likely to significantly increase inpatient throughput in the CT procedure room.
A key visual the team recommends to UPMC is a Pareto Chart, detailing causes of CT procedure room cancellations. CT procedures can be canceled for a variety of reasons, and this visual would give insight into the few causes that result in most of the cancellations. Those causes should then be targeted accordingly and minimized. The team recommends that UPMC keep a log of every time a slot in the CT procedure room goes unused, and mark the cause (patient consent, procedure moved to ultrasound, etc.). Upon documentation, UPMC could input the data into the Pareto chart template the team has created.
The benefits of this project are not strictly financial; they also improve patient satisfaction by lessening delays and extra hospital night stays. Ideally, patient throughput could be increased from 4.5 to 6 patients per day, as the current CT procedure room schedule has six slots per day. Overall, this project aligns with UPMC’s mission to provide high quality care, ensure operational excellence, and invest more resources into further improvement for all operations.

Project Summary
This project develops a discrete-event simulation in Simio to optimize the steel coil transportation process between the pickle line and cold mill at U.S. Steel’s Gary Works site in Indiana. Production delays and increased operating costs are caused by long truck wait times and operator idle times in the material handling process at this section of the facility. To approach this project, the DMAIC framework was chosen, as its phases outline the most methodical way to create a simulation. By analyzing six years of historical travel data, input distributions were derived to create a validated current state model using Simio software. Many alternatives were developed, with some including capital investments, and others strictly using the site’s current capabilities and resources. The alternatives – reducing the number of trucks used, purchasing one 150- ton truck, and improving driver behavior – were compared using statistical analysis (Bonferroni approach), a Pugh decision matrix, and cost-benefit analysis. The results indicate that reducing the number of trucks used is a fair alternative because it involves no investment. However, the purchase of one 150-ton truck yields the most benefits, as it eliminates wait time while still meeting the production target of 57 coils per turn. After the alternatives were analyzed, the U.S. Steel team was given an implementation plan for the 150-ton truck solution. By including a Simio model guide and the cost analysis, the project handoff to the U.S. Steel team is completed.
