Investigation of the effectiveness and safety of electrical stimulation
Investigation of the effectiveness and safety of electrical stimulation
Electrical stimulation via chronically implanted microelectrode arrays has been successfully used in humans for sensory restoration and can improve direct brain machine interface control of robotic prostheses. As promising as this therapy is, there are still major gaps in our understanding of the response to electrical stimulation in terms of both material degradation as well as the biological response. To address these gaps in our understanding we are studying both the material as well as biological response to chronic electrical stimulation with the goal of elucidating the most safe and effective forms of electrical stimulation.
This work includes studies comparing the activation efficiency of different electrode coatings such as iridium oxide and conducting polymer doped with carbon nanotubes in vivo via 2-photon microscopy as well as investigating the layer dependent response to different electrical microstimulation parameters by combining transparent microelectrode arrays with microprisms and 2-photon microscopy.
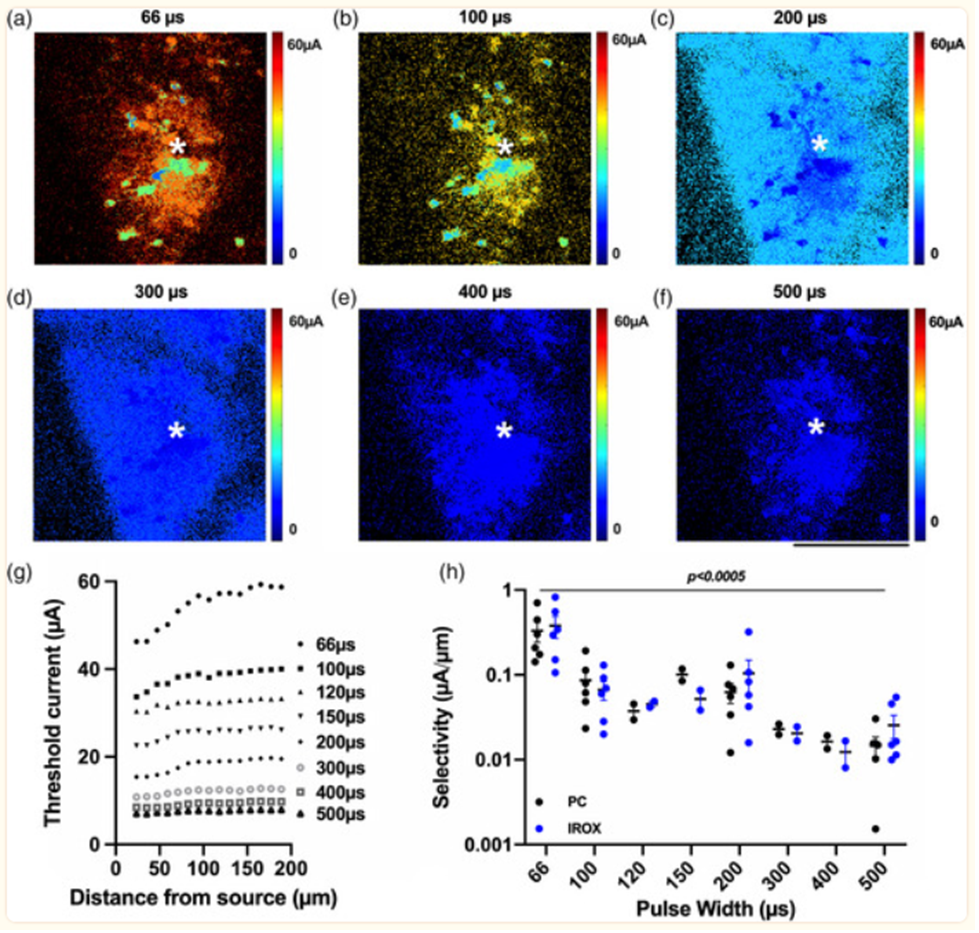
Effect of pulse width modulation on neuronal selectivity. Xiang et al., 2021.
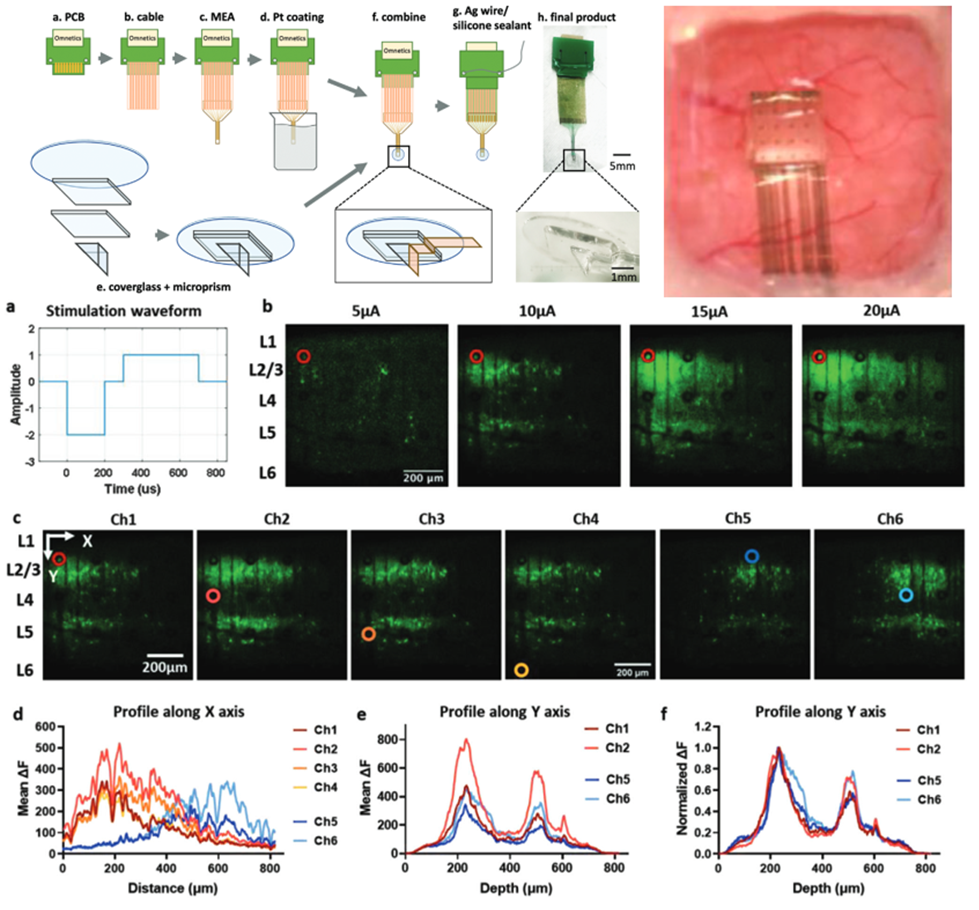
Integrated Microprism and Microelectrode Array for Simultaneous Electrophysiology and Two‐Photon Imaging Across all Cortical Layers. Yang et al., 2024
Relevant Publications:
- Yang, Q., Wu, B., Castagnola, E., Pwint, M. Y., Williams, N., Vazquez, A. L., & Cui, X. T. (2024). Integrated Microprism and Microelectrode Array for Simultaneous Electrophysiology and Two‐Photon Imaging Across all Cortical Layers. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2302362. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/adhm.202302362
- Williams, N. P., Kushwah, N., Dhawan, V., Zheng, X. S., & Cui, X. T. (2022). Effects of central nervous system electrical stimulation on non-neuronal cells. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 16, 967491. https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/neuroscience/articles/10.3389/fnins.2022.967491/full
- Zheng, X. S., Yang, Q., Vazquez, A., & Cui, X. T. (2022). Imaging the stability of chronic electrical microstimulation using electrodes coated with PEDOT/CNT and iridium oxide. IScience, 25(7). https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2589004222008100
- Zheng, X. S., Yang, Q., Vazquez, A. L., & Tracy Cui, X. (2021). Imaging the Efficiency of Poly (3, 4‐ethylenedioxythiophene) Doped with Acid‐Functionalized Carbon Nanotube and Iridium Oxide Electrode Coatings for Microstimulation. Advanced NanoBiomed Research, 1(7), 2000092. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8552016/
